Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Modeling an Arcade of Loops with the RTV Scaling Laws¶
This example shows how to model AIA emission from an arcade of semi-circular loops who’s thermal structure is modeled using the RTV scaling laws.
First, set up the coordinates for loops in the arcade.
Next, assemble the arcade.
strands = [synthesizAR.Loop(f'strand{i}', c) for i, c in enumerate(arcade_coords)]
arcade = synthesizAR.Skeleton(strands)
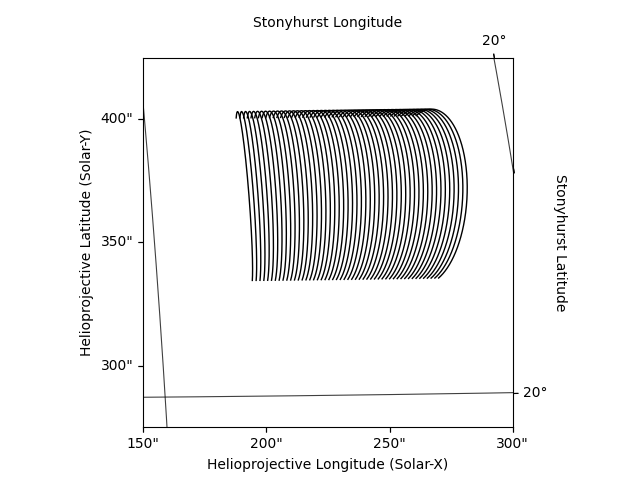
We can make a quick plot of what these coordinates would look like as viewed from Earth.
earth_observer = get_earth(obstime)
arcade.peek(observer=earth_observer,
axes_limits=[(150, 300)*u.arcsec, (275, 425)*u.arcsec])
Next, model the thermal structure of each loop using the RTV scaling laws.
rtv = RTVInterface(heating_rate=1e-6*u.Unit('erg cm-3 s-1'))
arcade.load_loop_simulations(rtv)
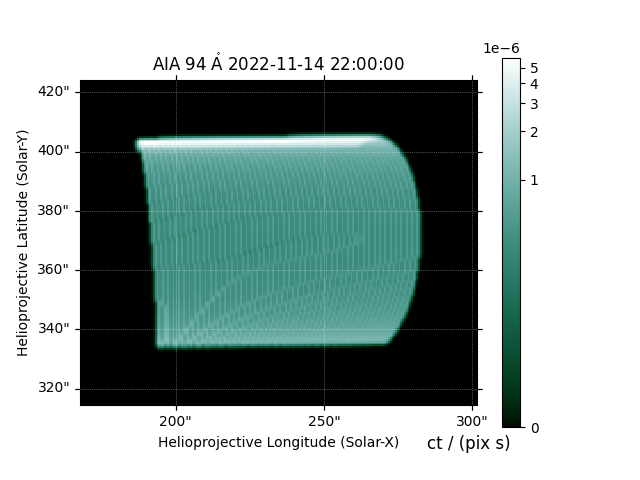
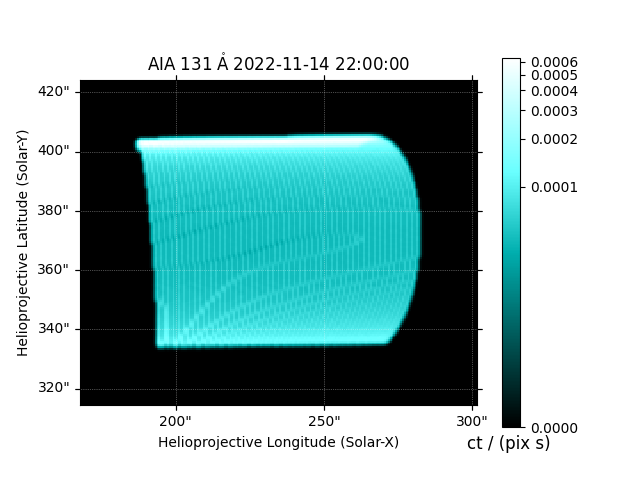
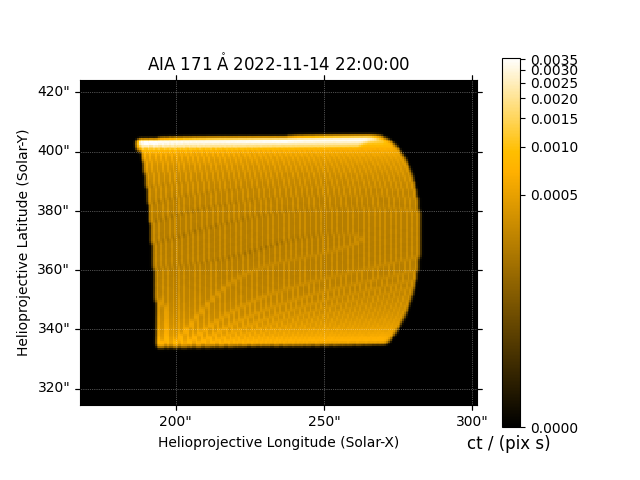
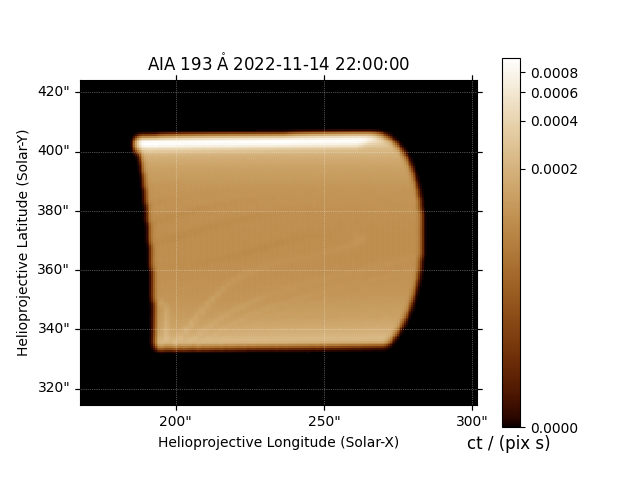
Finally, compute the LOS integrated AIA emission.
aia = InstrumentSDOAIA([0, 1]*u.s, earth_observer, pad_fov=(20, 20)*u.arcsec)
maps = aia.observe(arcade)
Files Downloaded: 0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?file/s]
aiapy.aia_V8_all_fullinst.genx: 0%| | 0.00/5.43M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
aiapy.aia_V8_all_fullinst.genx: 11%|█ | 593k/5.43M [00:00<00:00, 5.93MB/s]
aiapy.aia_V8_all_fullinst.genx: 69%|██████▉ | 3.73M/5.43M [00:00<00:00, 20.8MB/s]
Files Downloaded: 100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 3.01file/s]
Files Downloaded: 100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 3.00file/s]
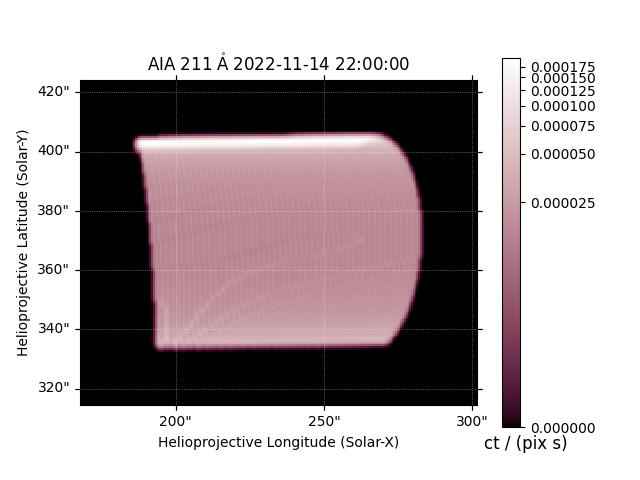
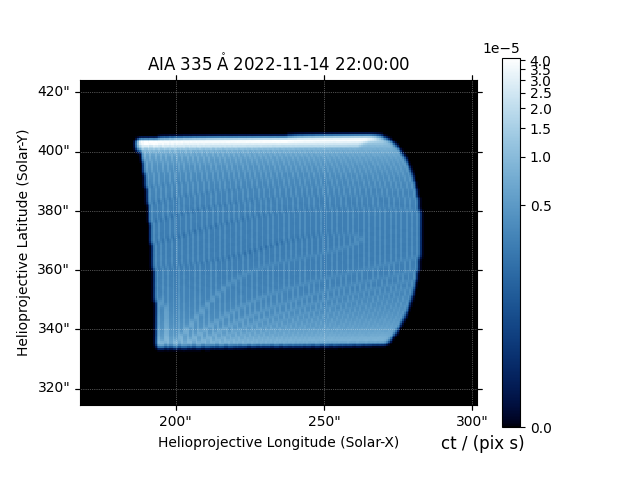
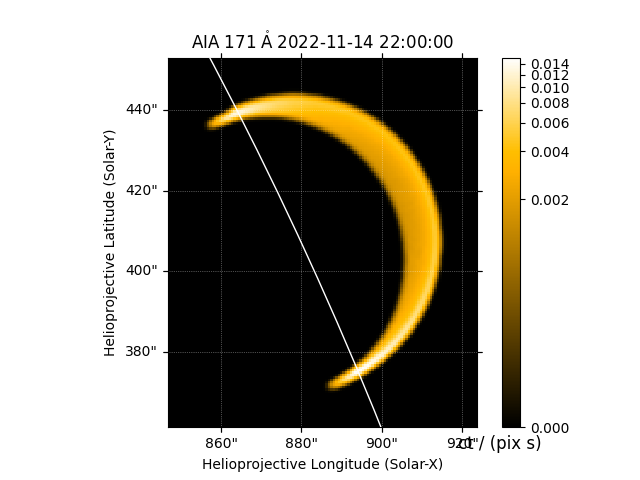
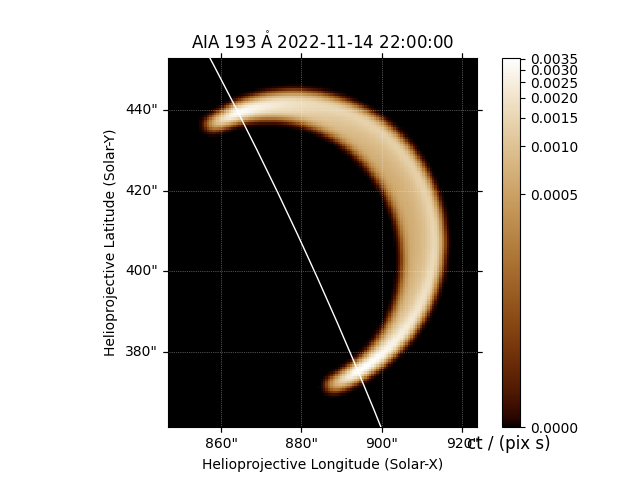
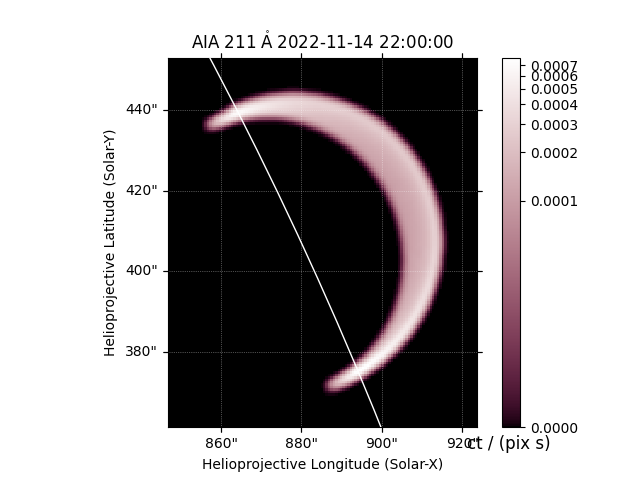
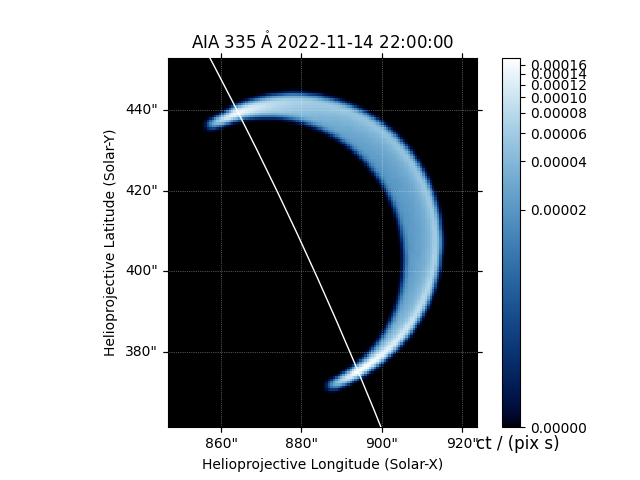
We can make a quick plot of what each EUV channel of AIA would look like.
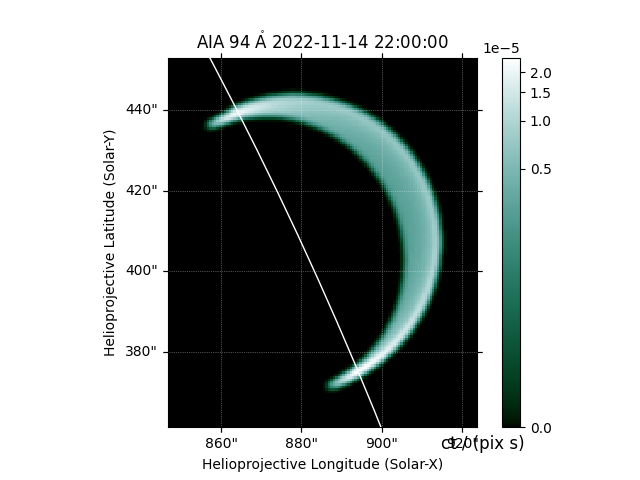
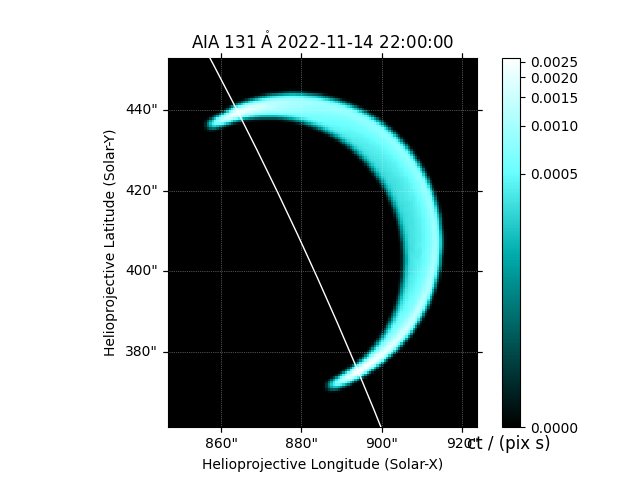
We can easily adjust the viewing angle to integrate the emission along a different LOS.
off_limb_observer = SkyCoord(
lon=-70*u.deg, lat=earth_observer.lat, radius=earth_observer.radius, frame=earth_observer.frame)
aia = InstrumentSDOAIA([0, 1]*u.s, off_limb_observer, pad_fov=(10, 10)*u.arcsec,)
maps = aia.observe(arcade)
for k in maps:
maps[k][0].peek(draw_limb=True)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 22.637 seconds)